Diabetes is one of the most common and feared diseases in the world. In the United States alone, nearly 8% of the entire population is believed to have diabetes. Diabetes is even more fearsome by its numerous complications like diabetic neuropathy. This is condition is characterized by damage to the nerves in various parts of the body, from the feet, legs, hands, digestive tract, sex organs and heart.
Types
There are four types of diabetic neuropathy—peripheral, autonomic, proximal and focal. The first type is the most common, with the feet and legs affected first then followed by the hands and arms. Peripheral neuropathy is characterized by extreme pain when walking, and a stinging sensation that worsens at night.
Autonomic neuropathy, on the other hand, can disrupt digestive and bladder function as well as sexual performance. It can also cause hypoglycemia unawareness, a disorder in which a person with diabetes no longer feels warning signs of low blood sugar. Proximal neuropathy causes pain in the lower torso particularly the thighs and hips, leading to weakness in the legs. The last type, focal neuropathy, causes muscle weakness or pain due to a sudden weakness of a group of nerves.
Symptoms
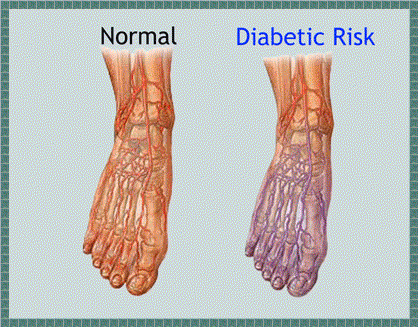 Generally speaking, diabetic neuropathy has symptoms such as numbness, pain and tingling sensation in the legs, feet, arms, and hands. People with diabetes who have this condition also suffer from indigestion, nausea and vomiting. They also have lower sexual interest, with men experiencing erectile dysfunction and women having vaginal dryness. They are also always fatigued, dizzy, and have problems urinating.
Generally speaking, diabetic neuropathy has symptoms such as numbness, pain and tingling sensation in the legs, feet, arms, and hands. People with diabetes who have this condition also suffer from indigestion, nausea and vomiting. They also have lower sexual interest, with men experiencing erectile dysfunction and women having vaginal dryness. They are also always fatigued, dizzy, and have problems urinating.
Nerve damage causes a person with diabetes to lose sensation in the arms and legs. As such, he may not even notice a small cut, or not even know that he has stepped on something sharp. Worst, damage to the nerves in the heart and blood vessels can prevent a patient from noticing chest pains that warn of an impending heart attack.
Causes
There are many causes of diabetic neuropathy, and scientists believe that a combination of factors trigger this condition. Metabolic factors like high blood sugar, abnormal levels of blood fat, and low insulin levels may give rise to diabetic neuropathy. Lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption and smoking can also lead to a diabetic to suffer from this condition. Genetics may also play a role, as those with a family history of diabetic neuropathy are more likely to acquire this disorder.
Treatment and Management
The most important step in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy is bringing down the blood sugar to normal levels. In doing so, further nerve damage is avoided. Blood sugar monitoring important as well. Meal planning, regular exercise and intake of insulin can all ensure that blood glucose levels are kept at an ideal range.
Certain medications are also prescribed by physicians to cure symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. A common prescription drug for pain caused by the disorder is Cymbalta, a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that is also used for treatment of generalized anxiety disorder and chronic muscle pain.
Share This